Primary Distribution system — Engineering Notes Online
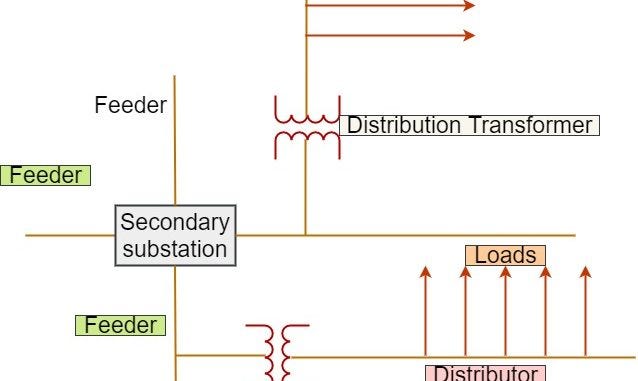
Primary distribution operates at the high voltage such as (3.3,6.6 and 11 KV).Primary distribution is usually carried out by 3-phase,3-wire system.Electric power from the generating station is transmitted through extra high tension transmission lines at voltage from 33 to 765 kv,to the substations.At the substations called secondary substations the voltage is stepped down to 11,6.6 or 3.3 KV with the help of power transformers for primary distribution.
The 33/11 kV secondary substations are usually located in the area having load requirement of the order of 5 MVA and normally a primary distribution line or a feeder is designed to carry a load of 1–2 MVA ,so the number of feeders originates from a secondary substation of 33/11 kV is 3–4.
For load requirement of the order of 8 MVA secondary transmission line is carried out at 66 kV and the number of feeders originates from a secondary substation of 66/11 kV is 6–8.
Fundamentally there are 4 different types of feeder layout:
- Radial Distribution Feeder
- Parallel Distribution Feeder
- Loop Distribution Feeder
- Network Distribution Feeder
1.Radial Distribution Feeder:

- Widely used in distribution system.
- Radial Feeder radiates from secondary substation(11kV) of a distribution substation.
- It branches into sub feeders and laterals extend into all parts of the area.
- Distribution transformer (11kV/415V) are connected to the primary feeders,sub feeders and laterals through fuse cut-outs.
- Power flows only in a single direction.


Radial Distribution Feeder
Advantages of Radial Distribution Feeder
- It is simplest,most economical and most commonly used .
- widely used in distribution system.
- Advantageous for supplying power to heavy industrial load near the secondary substation ,isolated loads such as tube wells and area of low density such as village.
Drawbacks of Radial Distribution Feeder
- Less reliability :There is only one path between the substation and the customer.so when a fault occurs at any point on the feeder,supply to all consumers beyond the fault point towards the tail end gets interrupted.
- If the load demand is to be increased the length of feeder has to be extended which may result in greater voltage drop.
2.Parallel Distribution Feeder

Parallel Distribution Feeder
- A parallel feeder has two radial feeders originates from the same or different secondary substations.
- Each feeder support half of the total load.
- Each feeder has capacity to carry full-load of the area.


Parallel Distribution Feeder
Advantages of Parallel Distribution Feeder
- Reliability is increased (as in the case of fault on one feeder the total load can be supplied by the healthy feeder).
- Widely used in developed countries.(Expensive than the radial feeders).
- Employed whenever the continuity of supply is of greater importance.
3.Loop Distribution Feeder
- Loop system consist of two or more radial feeders originating from the same or different secondary substations.
- Two paths between sources and customers.
- This system is often called European system.

Loop Distribution Feeder

Loop Distribution Feeder
Advantages of Loop Distribution Feeder
- Most reliable for continuity of supply and gives the better voltage regulation and less power losses.
- Feeders and loop components have sufficient reserve capacity to serve the load.
- Only slightly more complicated than a radial system.
Drawbacks of Loop Distribution Feeder
- Capacity and High cost:A loop must be able to meet all power and voltage drop requirements when fed from only one end not both.
4.Network Distribution Feeder


Network Distribution Feeder
Network Distribution Feeder
- Feeder rings main is energized from two or more than two generating stations or substations.
- Power can be supplied to all the distribution transformers even though a part of network may be out of service.
- Provides the better reliability and flexibility.
- Much more complicated than other forms of feeder layout and thus are more difficult to analyze.
- And are used in large metropolitan cities where continuity of supply is the most important.
For more Related Terms:
- Transformer
- Voltage regulation of Transformer
- Distribution system design
- Sag and Tension in overhead transmission line
- Power System Structure
- Transformer Efficiency
- HVDC Transmission
- Substations and its types
For More Articles on Electrical Engineering:
https://www.notesforengineering.com/power-factor-improvement/
Originally published at https://engineeringnotesonline.com on September 1, 2020.